Quantum Optics and Informatics Practicum
The educational and scientific complex for practical work in quantum optics and informatics allows to study the quantum physics basic laws experimentally, quantum informatics problems being an example. These problems are solved on the simpliest and most intuitive physical platform — quantum optics platform.
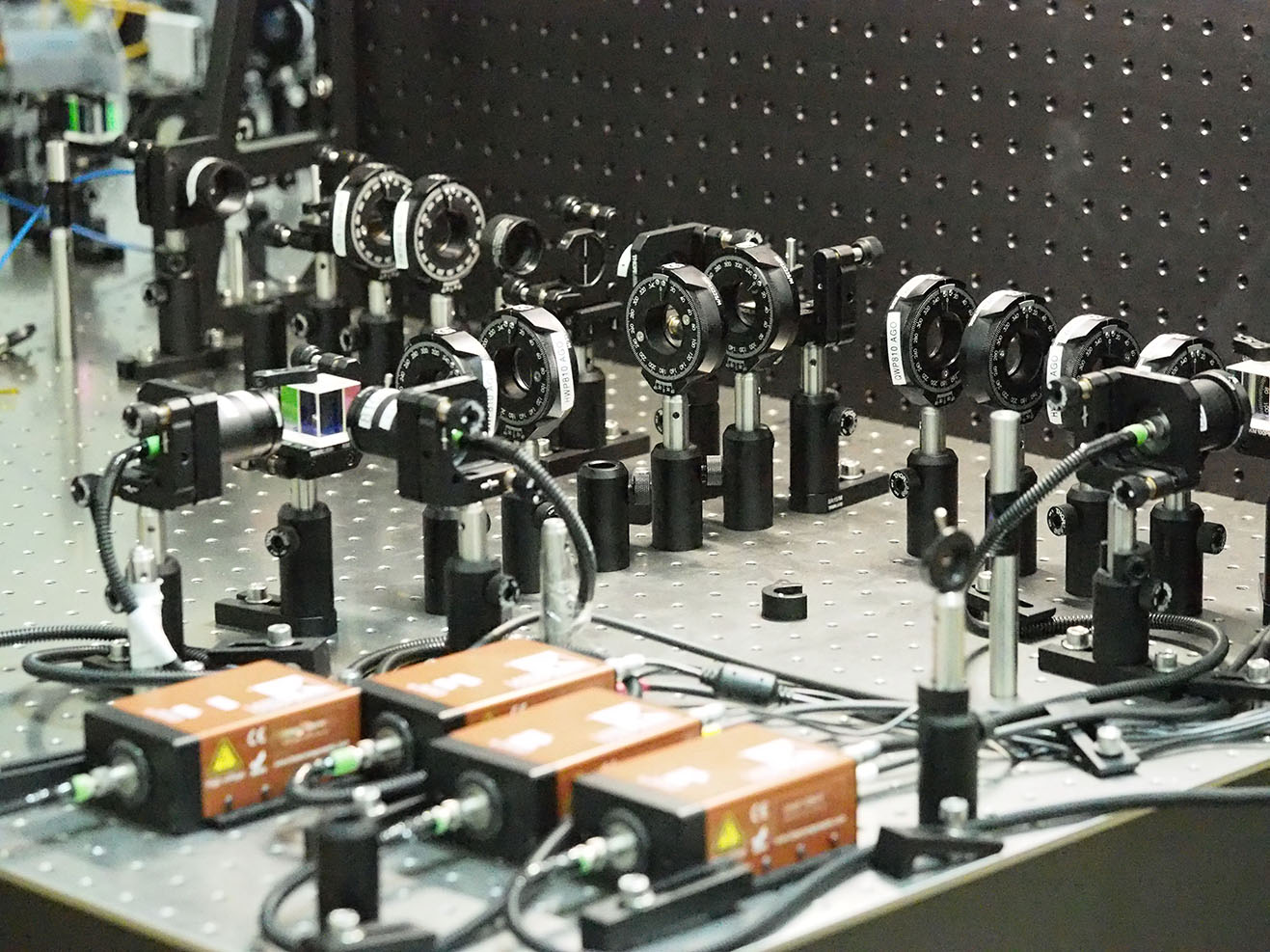

Quantum Simulator Based on Single Neutral Atoms
Digital quantum simulator is a device to execute specialized quantum algorithms for modelling other quantum systems and for solving a wide range of optimization problems.
One of the quantum simulator prototypes which is being developed at the MSU QTC is based on a quantum register of single rubidium atoms captured in an array of optical tweezers. This technology makes it possible to create 2D atoms arrays with controlled interactions that can be used as physical qubits in a quantum simulator.
A cloud access system to the developed simulator will soon be implemented.
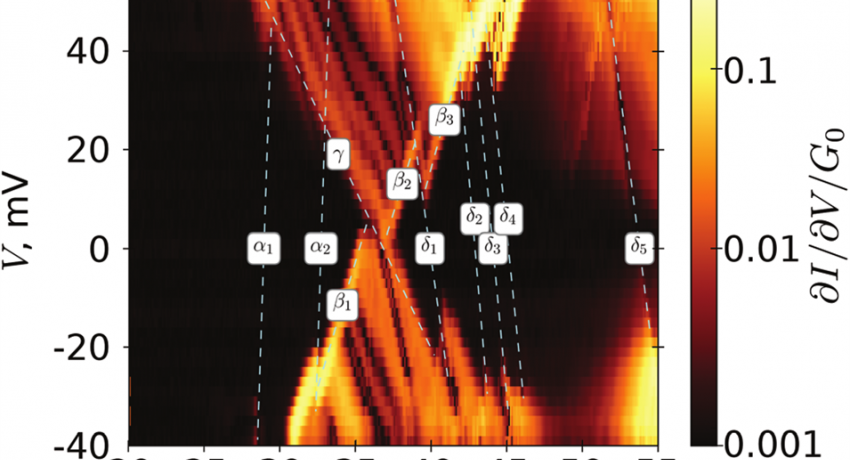
Single-Atom Single-Electron Transistor
A solid-state single-atom single-electron transistor is produced on a single-crystal semiconductor or dielectric substrate surface, where single impurity atoms are preliminarily implanted in the surface layer. The drain and source electrodes are placed on the crystal surface such that single-electron tunneling between the drain and source electrodes and the impurity atom (which is the working charge centre) becomes possible. Gate electrodes are created on the substrate surface at a distance from the impurity atom that excludes the tunneling possibility.
Reprogrammable Multi-Channel Interferometers
Reprogrammable multi-channel interferometers are the tool for new approaches to information processing, both classical and quantum. Until recently, reprogrammable interferometers were created using architectures (i.e., methods of elementary blocks combining) which are sensitive to errors that occur at the manufacture stage.
Linear Optical Quantum Simulator
Linear optical quantum simulator is based on single-photon quantum states. Multiphoton states are transformed by a programmable linear optical interferometer and then the output is measured by single photon counters. In such a system, logical-state-space dimension can be very large that makes it possible to realize computational advantage over classical computers in a number of tasks.
Quantum Technology Startups Support Programme
The programme is aimed at mentoring and organizational startups support in preparation for a potential investor pitching, or for an external startup support competition participation.
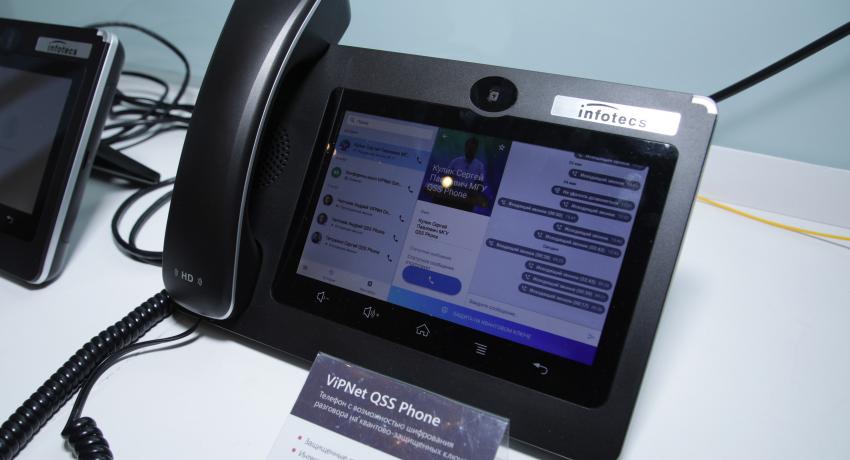
ViPNet QSS "Quantum" Phone
Quantum Technology Centre together with the InfoTeCS company is developing and creating a device providing secure document management based on quantum keys. The device allows secure exchange of voice messages, files, and communication via video calls.
The pre-series sample of the first in Russia "quantum" phone ViPNet QSS Phone, which is part of the ViPNet Quantum Security System (ViPNet QSS), was demonstrated by InfoTeCS and the Faculty of Physics MSU Quantum Technology Centre on May 28, 2019.